

In This Article
In This Article
A DNA kit can connect you with new relatives, map migrations, or flag health traits—but only if you choose the right test. Understanding how each kit works helps you invest wisely and set realistic expectations.
Know Your DNA Reviews

Don't miss out on the opportunity to learn more about yourself. Read our best DNA test page to find the best one for you.
Imagine shuffling two decks—half from Mom, half from Dad. Autosomal tests read that mixed deck across your 22 non-sex chromosomes. Because the shuffle changes each generation, the test can confirm relationships out to about fifth- or sixth-cousin range.
Major services like AncestryDNA, 23andMe, MyHeritage, and FamilyTreeDNA all lead with autosomal kits because every person can take one and the databases are largest. If you want a broader introduction, our explainer on DNA testing basics walks through costs, sample types, and privacy tips.
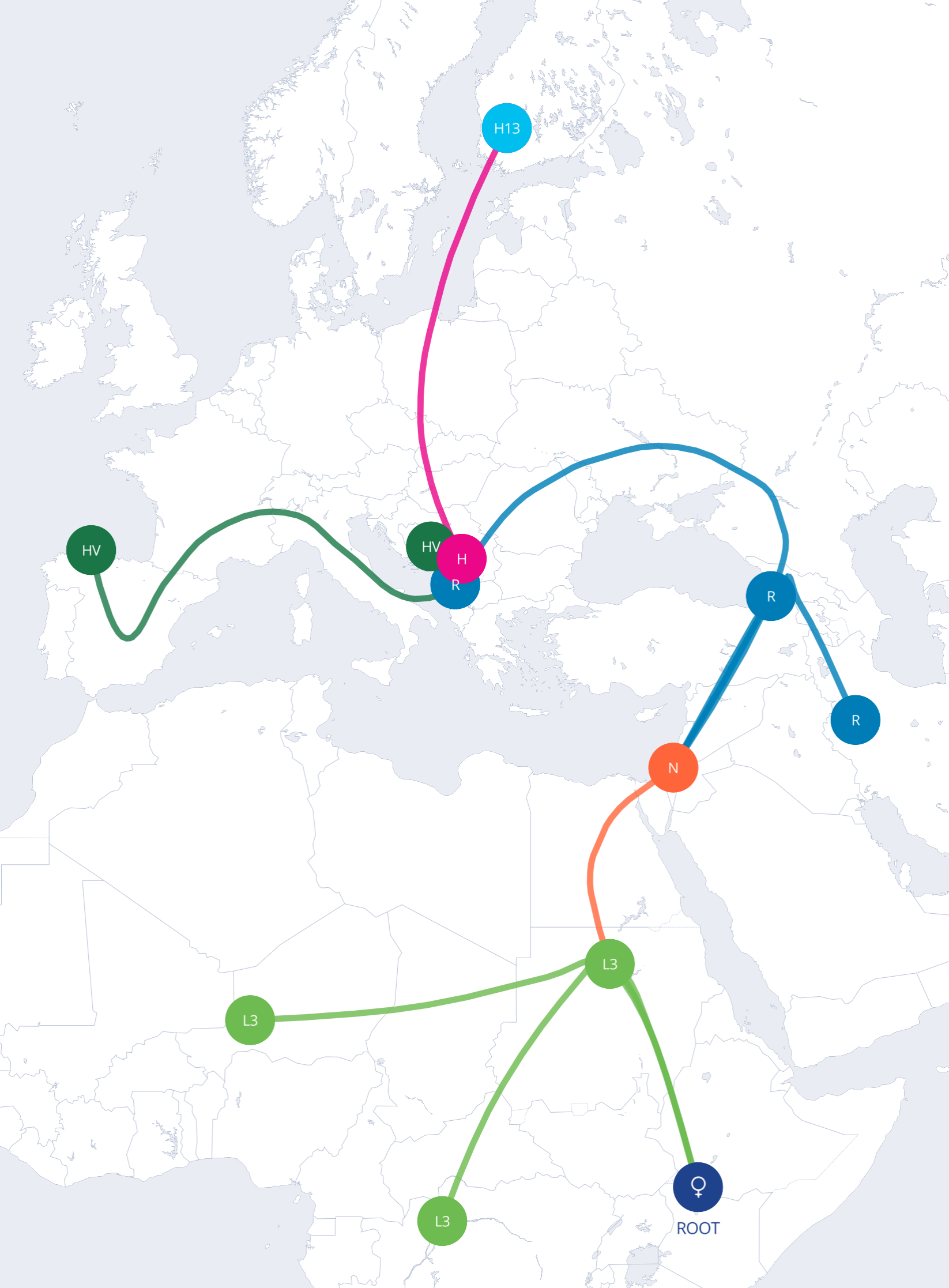
Think of a surname that passes from father to son; the Y chromosome travels the same route. A Y-DNA kit scans markers on that chromosome, which changes slowly over centuries.
| Why pick Y-DNA? | What you gain |
| Haplogroup assignment | Places your paternal line on humanity’s migration map |
| Deep time depth | Tracks a single line tens of thousands of years back |
| Surname checks | Confirms whether two men share a direct paternal ancestor |
FamilyTreeDNA offers tiered Y panels, while some broader kits include a basic Y overview.
Your mitochondria are tiny power plants carrying a tag from your mom. Because this DNA rarely mixes, it leaves a clear maternal breadcrumb trail.
For a step-by-step look at sample collection and result interpretation, see our guide on mitochondrial DNA testing.
| Your Question | Best Test | Typical Time Depth | Who Can Take It? |
| “I want to find living cousins.” | Autosomal | Up to ~200 years | Everyone |
| “Did my surname line come from Scotland?” | Y-DNA | 1,000s of years | Biological males |
| “Where did my mother’s line begin?” | mtDNA | 1,000s of years | Everyone |
If cousin matches are top priority, start with autosomal. When you hit a brick wall on one line, add Y-DNA or mtDNA for extra clues.
Think of clinical testing as preventive medicine, not family history. Doctors order targeted panels or whole-exome sequencing to diagnose conditions, predict risks, or guide drug choices. Results often trigger lifestyle changes or medical surveillance—and they always come with professional counseling.
Law-enforcement labs use STR markers to identify people, link crime-scene samples, or reunite disaster victims with families. These profiles examine different parts of the genome than consumer kits and rarely reveal ancestry.
One size rarely fits all. Consider three factors before you buy:
| Company | Test Types | Database Size | Stand-out Feature |
| AncestryDNA | Autosomal | ~23 million | Largest family-tree tools |
| 23andMe | Autosomal + basic Y/mtDNA | ~14 million | Health trait reports |
| FamilyTreeDNA | Autosomal, Y, mtDNA | ~2 million | Deep lineage panels |
| MyHeritage | Autosomal | ~7 million | Strong European matches |
For a fuller rundown of price and privacy, our latest AncestryDNA kit review breaks down pros and cons.
Start with your goal:
Treat each kit as one tool in a growing toolbox. The right combination—and a bit of document research—can turn raw code into rich family stories.
Know Your DNA Reviews
Looking for a DNA test that's accurate and can tell you about your health and heritage?

