
In This Article
In This Article
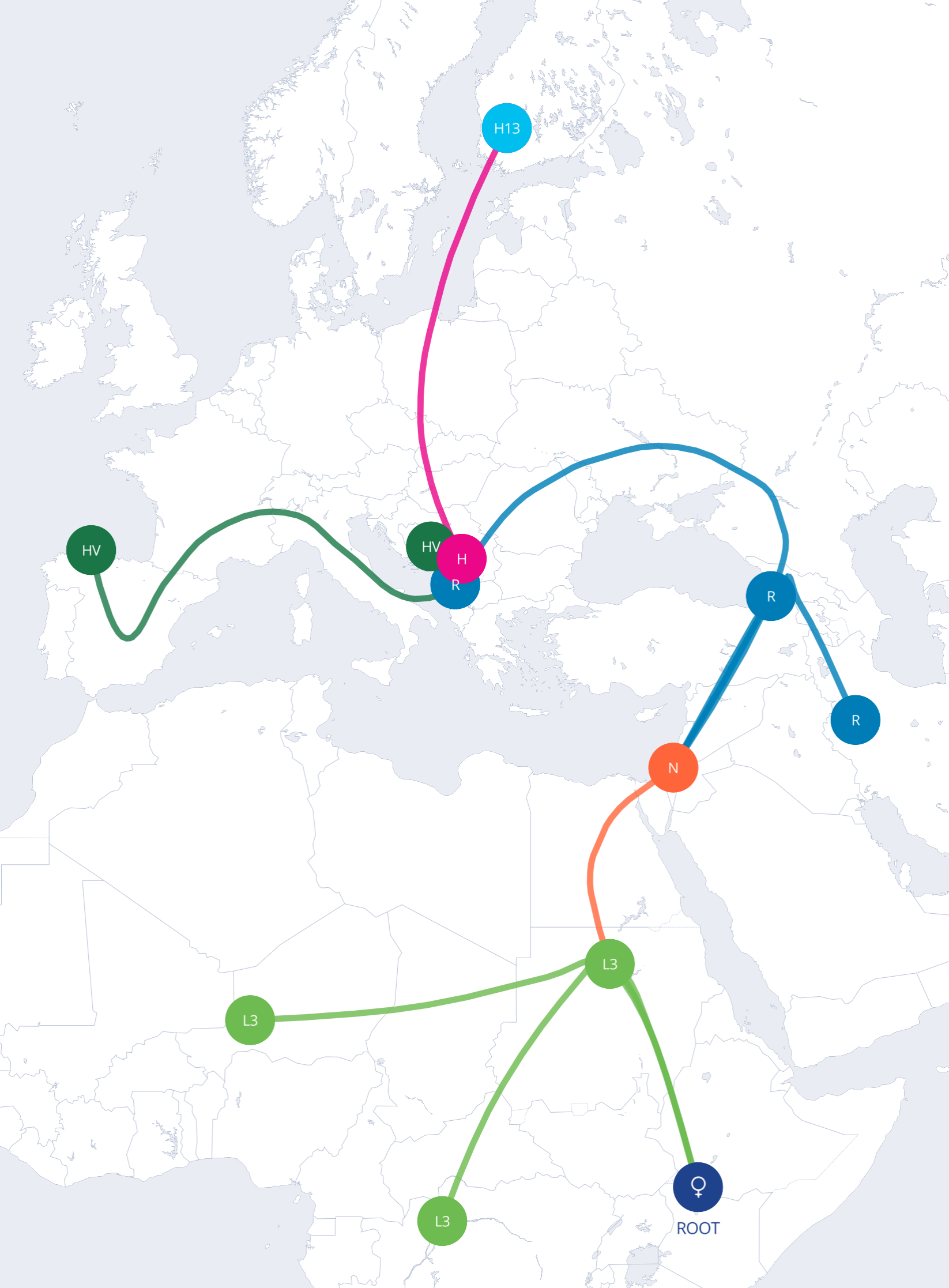
An extensive amount of evidence supports the theory that modern humans can trace their origins back to Africa. In this article, we’ll take a look at the genetic, fossil, and archaeological evidence supporting this theory.
Studies show that the first anatomically modern humans emerged in Africa, and migrations from there spread our species across the globe. When populations left Africa, they carried only a subset of the genetic diversity found within Africa itself.
This is why people of non-African descent tend to have less overall genetic variation. Individuals of European or Asian descent often have around 1-4% of their DNA from Neanderthals who lived outside Africa.
Those of primarily African descent have significantly less neanderthal DNA, highlighting that interbreeding happened after the out-of-Africa migrations.
Anthropologists and geneticists agree on several key findings:
Know Your DNA Reviews

Don't miss out on the opportunity to learn more about yourself. Read our best DNA test page to find the best one for you.
While all humans trace their ancestry back to Africa, the exact percentage of African DNA in any individual varies greatly. Factors like later migrations and interbreeding create a complex picture.
Additionally, recent studies suggest multiple origins within Africa rather than a single starting point.
Though everyone has African ancestors, the percentage of African DNA within a person's genome depends on their specific lineage and the complex interplay of migrations and interbreeding throughout history.
All humans share common ancestors rooted in Africa. However, a DNA test result might show you have 0% African heritage.
Due to genetic drift, DNA segments gradually shifted over generations. Think of genetic drift as randomly removing beads from a jar each generation; over time, the color distribution shifts noticeably.
Your DNA results reveal ancestry at different depths in your genetic timeline. Recent ancestry (from the last 5–10 generations) shows clearly on autosomal DNA tests, while deeper history, stretching thousands of years back, is better seen through specialized markers called haplogroups.
A haplogroup is like a genetic signature passed down your maternal (mtDNA) or paternal (Y-DNA) lines. Unlike autosomal percentages, haplogroups remain stable over many generations, tracing back tens of thousands of years.
When reviewing your results, consider combining your autosomal percentages with haplogroup data. If you’re considering getting a second perspective or refining your results, compare affordable DNA kits to find the best option.
Ancestry discussions often include persistent misconceptions. Let's clarify some common ones:
| Misconception | Reality |
| Everyone has the same percentage of African DNA. | Percentages vary widely due to recombination and individual family histories. |
| "0% African" means no African ancestry at all. | Typically, it means segments are too old or small to detect, not that they don’t exist. |
| You can pinpoint a single African tribe for each person. | Ancient lineages usually predate current ethnic and tribal groupings. |
For more clarity, see our primer on DNA test accuracy.
Know Your DNA Reviews
Looking for a DNA test that's accurate and can tell you about your health and heritage?
